[ad_1]
Xrdp is an open-source implementation of the Microsoft Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) that allows you to graphically control a remote system. With RDP, you can log in to the remote machine and create a real desktop session the same as if you had logged in to a local machine.
This tutorial covers how to install and configure Xrdp server on Ubuntu 20.04.
Installing Desktop Environment #
Ubuntu servers are managed from the command line and do not have a desktop environment installed by default. If you run the desktop version of Ubuntu, skip this step.
There are various desktop environments available in Ubuntu repositories that you can choose. One option is to install Gnome, which is the default desktop environment in Ubuntu 20.04. Another option is to install Xfce
. It is a fast, stable, and lightweight desktop environment, which makes it ideal for usage on a remote server.
Run one of the commands below to install the desktop environment of your choice.
Depending on your system, downloading and installing GUI packages will take some time.
Installing Xrdp #
Xrdp is incuded in the default Ubuntu repositories. To install it, run:
sudo apt install xrdp Once the installation is complete, the Xrdp service will automatically start. You can verify it by typing:
sudo systemctl status xrdpThe output will look something like this:
● xrdp.service - xrdp daemon
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/xrdp.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2020-05-22 17:36:16 UTC; 4min 41s ago
...
By default Xrdp uses the /etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key file that is readable only by members of the “ssl-cert” group. Run the following command to add the xrdp user to the group
:
sudo adduser xrdp ssl-cert Restart the Xrdp service for changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart xrdpThat’s it. Xrdp has been installed on your Ubuntu server, and you can start using it.
Xrdp Configuration #
The Xrdp configuration files are located in the /etc/xrdp directory. For basic Xrdp connections, you do not need to make any changes to the configuration files.
Xrdp uses the default X Window desktop environment (Gnome or XFCE).
The main configuration file is named xrdp.ini
. This file is divided into sections and allows you to set global configuration settings such as security and listening addresses and create different xrdp login sessions.
Whenever you make any changes to the configuration file, you need to restart the Xrdp service.
Xrdp uses startwm.sh file to launch the X session. If you want to use another X Window desktop, edit this file.
Configuring Firewall #
The Xrdp daemon listens on port 3389 on all interfaces. If you run a firewall on your Ubuntu server
, you’ll need to open the Xrdp port.
To allow access to the Xrdp server from a specific IP address or IP range, for example, 192.168.33.0/24, you would run the following command:
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.33.0/24 to any port 3389If you want to allow access from anywhere (which is highly discouraged for security reasons), run:
sudo ufw allow 3389For increased security, you may consider setting up Xrdp to listen only on localhost and creating an SSH tunnel
that securely forwards traffic from your local machine on port 3389 to the server on the same port.
Connecting to the Xrdp Server #
Now that you have set up your Xrdp server, it is time to open your Xrdp client and connect to the server.
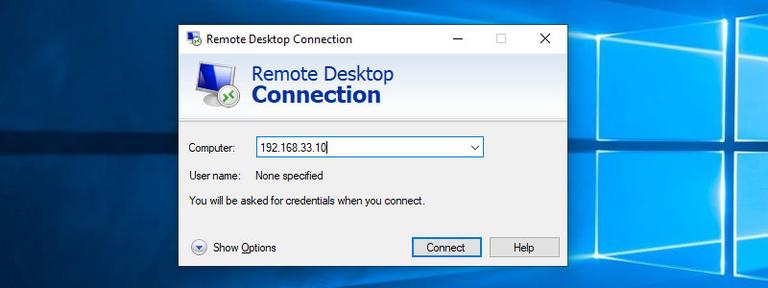
If you have a Windows PC, you can use the default RDP client. Type “remote” in the Windows search bar and click on “Remote Desktop Connection”. This will open up the RDP client. In the “Computer” field, enter the remote server IP address and click “Connect”.
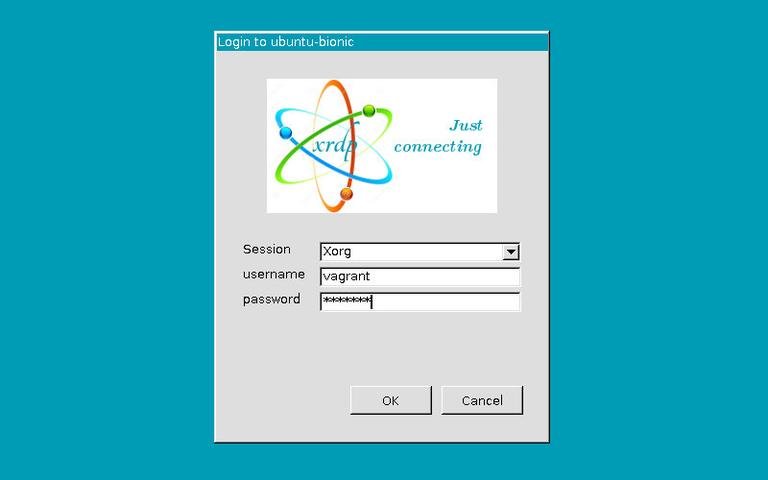
On the login screen, enter your username
and password and click “OK”.
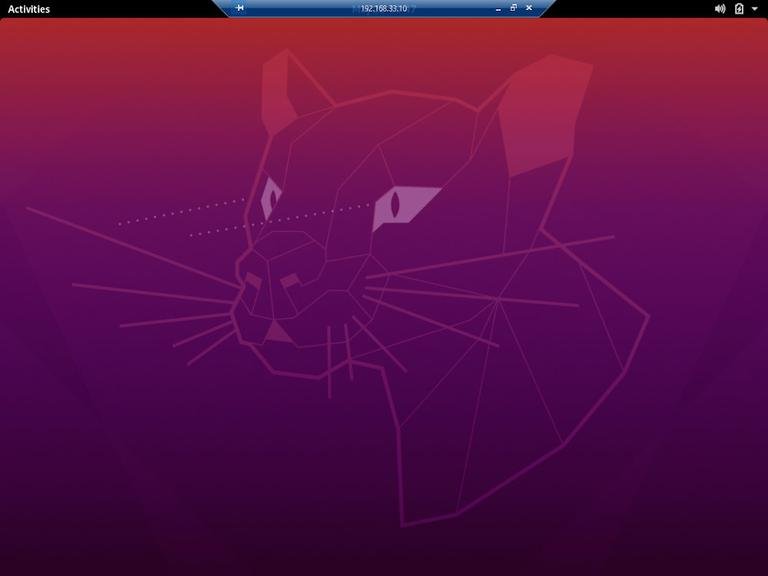
Once logged in, you should see the default Gnome or Xfce desktop. It should look something like this:
You can now start interacting with the remote desktop from your local machine using your keyboard and mouse.
If you are running macOS, you can install the Microsoft Remote Desktop application from the Mac App Store. Linux users can use an RDP client such as Remmina or Vinagre.
Conclusion #
Configuring a remote desktop allows you to manage your Ubuntu 20.04 server from your local machine through an easy to use graphic interface.
If you have questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
[ad_2]
Source link