[ad_1]
Redmine is a free and open-source project management and issue tracking application. It is cross-platform and cross-database and built on top of the Ruby on Rails framework.
Redmine
includes support for multiple projects, wikis, issue tracking system, forums, calendars, email notifications, and much more.
This tutorial explains how to install and configure the latest version of Redmine on CentOS 8. We’ll use MariaDB as a database back-end and Passenger + Apache as a Ruby application server.
Prerequisites #
Ensure that you have met the following prerequisites:
Creating a MySQL database #
Redmine supports MySQL/MariaDB, Microsoft SQL Server, SQLite 3, and PostgreSQL
. We’ll use MariaDB as a database back-end.
If you don’t have MariaDB or MySQL installed on your CentOS server, you can install it by following these instructions
.
Login to the MySQL shell using the following command:
sudo mysqlFrom within the MySQL shell, run the following SQL statements to create a new database
, new user, and grant the user access to the database
:
CREATE DATABASE redmine CHARACTER SET utf8;GRANT ALL ON redmine.* TO 'redmine'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'change-with-strong-password';
Make sure you change change-with-strong-password with a strong password.
Once done, exit the MySQL shell:
EXIT;Installing Passenger, Apache and Ruby #
Passenger
is a fast and lightweight web application server for Ruby, Node.js, and Python that can be integrated with Apache
and Nginx. We will install Passenger as an Apache module.
Enable the EPEL repository
:
sudo dnf install epel-releasesudo dnf config-manager --enable epel
Once the repository is enabled, update the packages list and install Ruby, Apache and Passenger:
sudo dnf install httpd mod_passenger passenger passenger-devel rubyStart the Apache service and enable it to start on boot:
sudo systemctl enable httpd --nowCreating New System User #
Create a new user and group, with home directory /opt/redmine that will run the Redmine instance:
sudo useradd -m -U -r -d /opt/redmine redmineAdd the apache user to the redmine group
and change the /opt/redmine directory permissions
so that the Apache can access it:
sudo usermod -a -G redmine apachesudo chmod 750 /opt/redmine
Installing Redmine #
At the time of writing, the latest stable version of Redmine is version 4.1.0.
Before continuing with the next steps, visit the Redmine download page
to see if a newer version is available.
Install the GCC compiler and libraries required to build Redmine:
sudo dnf group install "Development Tools"sudo dnf install zlib-devel curl-devel openssl-devel mariadb-devel ruby-devel
Make sure you are running the following steps as redmine user:
sudo su - redmine1. Downloading Redmine #
Download the Redmine archive with curl
:
curl -L http://www.redmine.org/releases/redmine-4.1.0.tar.gz -o redmine.tar.gzOnce the download is completed, extract the archive:
tar -xvf redmine.tar.gz2. Configuring Redmine Database #
Copy
the Redmine example database configuration file:
cp /opt/redmine/redmine-4.1.0/config/database.yml.example /opt/redmine/redmine-4.1.0/config/database.ymlOpen the file with your text editor:
nano /opt/redmine/redmine-4.1.0/config/database.ymlSearch for the production section and enter the MySQL database and user information we created previously:
/opt/redmine/redmine-4.1.0/config/database.yml
production:
adapter: mysql2
database: redmine
host: localhost
username: redmine
password: "change-with-strong-password"
encoding: utf8mb4Once done, save the file and exit the editor.
3. Installing Ruby dependencies #
Switch
to the redmine-4.1.0 directory and install the Ruby dependencies:
cd ~/redmine-4.1.0gem install bundler --no-rdoc --no-ribundle install --without development test postgresql sqlite --path vendor/bundle
4. Generate Keys and Migrate the Database #
Run the following command to generate keys and migrate the database:
bundle exec rake generate_secret_tokenRAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rake db:migrate
Configuring Apache #
Switch back to your sudo user and create the following Apache vhost
file:
exitsudo nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/example.com.conf
/etc/httpd/conf.d/example.com.conf
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName example.com
ServerAlias www.example.com
DocumentRoot /opt/redmine/redmine-4.1.0/public
<Directory /opt/redmine/redmine-4.1.0/public>
Options Indexes ExecCGI FollowSymLinks
Require all granted
AllowOverride all
</Directory>
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/example.com-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/example.com-access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Don’t forget to replace example.com with your Redmine domain.
Restart the Apache service
by typing:
sudo systemctl restart httpdConfigure Apache with SSL #
If you don’t have a trusted SSL certificate for your domain, you can generate a free Let’s Encrypt SSL certificate by following these instructions
.
Once the certificate is generated, edit the Apache configuration as follows:
sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/example.com.conf/etc/httpd/conf.d/example.com.conf
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName example.com
ServerAlias www.example.com
Redirect permanent / https://example.com/
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName example.com
ServerAlias www.example.com
Protocols h2 http/1.1
<If "%{HTTP_HOST} == 'www.example.com'">
Redirect permanent / https://example.com/
</If>
DocumentRoot /opt/redmine/redmine-4.1.0/public
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/example.com-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/example.com-access.log combined
SSLEngine On
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem
<Directory /opt/redmine/redmine-4.1.0/public>
Options Indexes ExecCGI FollowSymLinks
Require all granted
AllowOverride all
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Accessing Redmine #
Open your browser
, type your domain, and assuming the installation is successful, a screen similar to the following will appear:
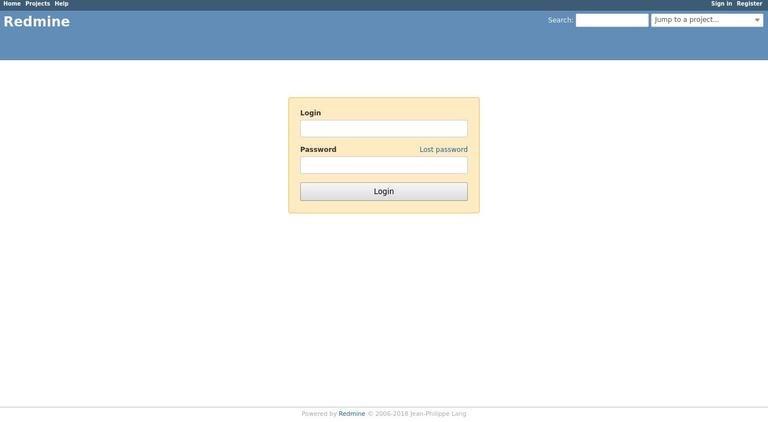
The default login credentials for Redmine are:
- Username: admin
- Password: admin
When you log in for the first time, you will be prompted to change the password, as shown below:
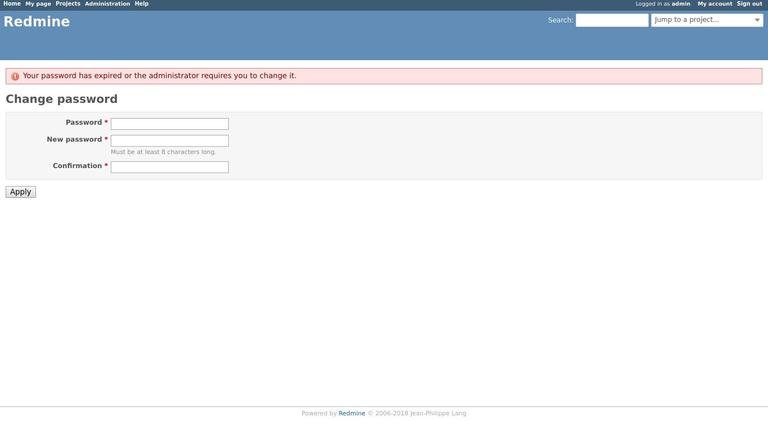
Once you change the password, you will be redirected to the user account page.
If you can’t access the page, then probably your firewall
is blocking port Apache ports.
Use the following commands to open the necessary port:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=443/tcpsudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=80/tcpsudo firewall-cmd --reload
Conclusion #
You have successfully installed Redmine on your CentOS system. You should now check the Redmine Documentation
and learn more about how to configure and use Redmine.
If you hit a problem or have feedback, leave a comment below.
[ad_2]
Source link